
QSAS: A Science Analysis System for Space Plasma Data
Data Handling
Contents
QSAS allows the ingestion of data from a variety of
sources. In all cases, the result of data ingestion is to place
one or more data objects onto the Working List.
The Data Selector (the hierarchical view of databases), Open Data File (Direct Import and browse of data files) and Write Data File (data export with join onto common timeline) menu items are accessed through the File pull-down menu on the QSAS Main Window.
Currently supported file formats include Cluster
Exchange Format (CEF) files, Common Data
Format (CDF) files (which should conform to at least ISTP
standard, though
others may also be imported) and QSAS Flat ASCII files as
specified in the
documentation accompanying QSAS. This file format relies on simple
ASCII
headers (either attached to the file or co-located) which include
the
capability to specify quite general time formats. Thus many (most)
foreign
ASCII files can be read by QSAS after writing an appropriate
header. Such
direct access to files enables variables to be ingested one at a
time. The
direct file interface allows the data values and metadata to be
browsed before
import.
Limited PDS format read capability is also provided
(.TAB and .LBL files) although helper files are required for most
Rosetta RPC files.
The results of calculations performed within QSAS may also be saved by exporting them from the Working List. QSAS supports the export of Cluster Exchange Format (CEF) files, ISTP/Cluster-compliant CDF files and flat ASCII files (tabular or delimited). If multiple time-series objects are exported, QSAS will join them onto a common time line using algorithms chosen by the user.
Data may be ingested into QSAS by opening a
file directly or using the Data
Selector database view.
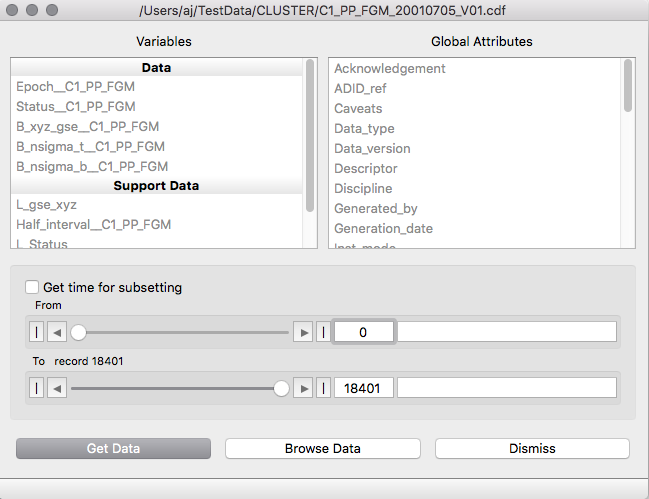
The Open Data File option brings up a file
selector. When a file is opened a list of the variables in the
file will be presented, and double clicking a variable or
selecting the Get Data button will ingest that data
variable along with all its metadata including timetags. The
Window remains open for further imports from the same data file
and must be dismissed manually. Data may be restricted to a range
of records (or time interval) using the From and To
time sliders.
Selecting a Global Attribute will open an
object browser display for that
attribute. Pressing the Browse Data button will open an object browser display
showing the data
and a list of cross references from which individual attributes
may be selected
and displayed.
The Data
Selector is a more powerful interface for
frequently-used databases and gives a hierarchical view of the
data, which enables
the user to determine the availability of data simultaneously from
several
sources and retrieve data for selected intervals without the
needing to know their
locations or file names.
Data files that have insufficient or incorrect metadata for use within QSAS may need Helper Files
When either Direct Import or the Data Selector is used to read data QSAS will also search the directory containing the data file for any files with suffix ".qat". All such helper files found in the directory will be read after the data file and before a variable is placed on the working list. The helper files have the same syntax for attributes contained within variable blocks as cef files. Any attribute information in a variable block will be attached to a variable if it has the same name as the variable block identifier. If the attribute is already present it will be replaced - thus a helper file can be used to correcct metadata as well as add it. No other information about a variable can be read from a helper file, and in this respect it differs from a detached header file. Care must be taken with helper files as the attribute information will be available to any file in the same directory and will silently be applied if the file contains a variable with the same name as one of the variable blocks. Multiple helper files may be placed in a directory and all of them will be read. There is no guarantee of reading order, and hence no control over which helper file takes precedence if a conflict arises.
Helper files should be used sparingly and kept in a dedicated directory containing the data set to which they apply. A sample helper file "ThemisFGM.qat" can be found in the examples directory in the QSAS installation. This shows the syntax for modifying metadata for three of the variables in Themis sample FGM cdf files.
Data objects on the Working List, regardless of whether they have been imported from other data files or created by analysis within QSAS, can be exported to files by choosing Export from the File menu on the Working List. This brings up the Export User Interface as shown. Data Objects to be exported must be dragged or copied and pasted from the Working List (or any other list view showing an object held on the working list) to the export list. Objects on the export list can be grouped into folders.
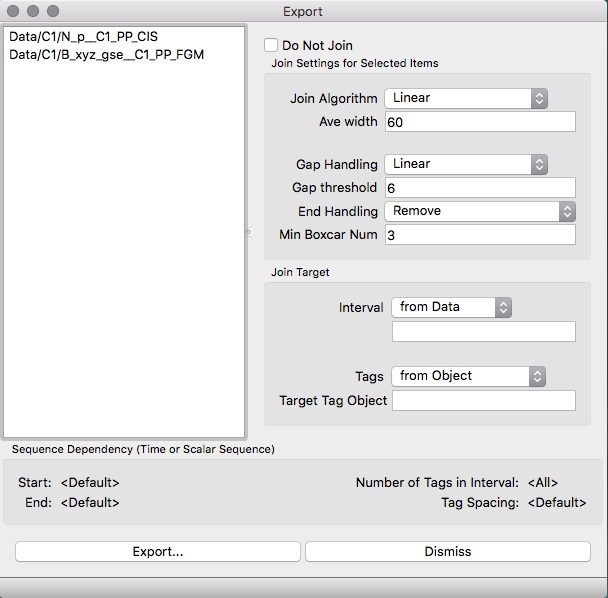
Time Series data objects will be exported together by joining them onto a SINGLE set of time tags, so the source of these tags must be specified (by default the first time series data object is used as the timetag source). The behaviour of this window is identical to the join window. The user may also specify a time interval for the export (i.e., to export only a subset of the data) using a time series data object, a time interval object, or the Time Editor. Since more than one Time Series object may be exported, they must be joined onto the common time tags using either linear interpolation or boxcar averaging, with data gaps filled or removed (see the Analysis section for more details).
Join options will be applied to
any selected items or folders, and different choices may be made
for different
selections. The time tag and time interval for the exported data
apply to all
items being exported as QSAS unless Do Not Join is
selected. In the case that data are not joined and of different
lengths the export window will give an option to pad to the same
length. Only a CDF file may have variables of different lengths.
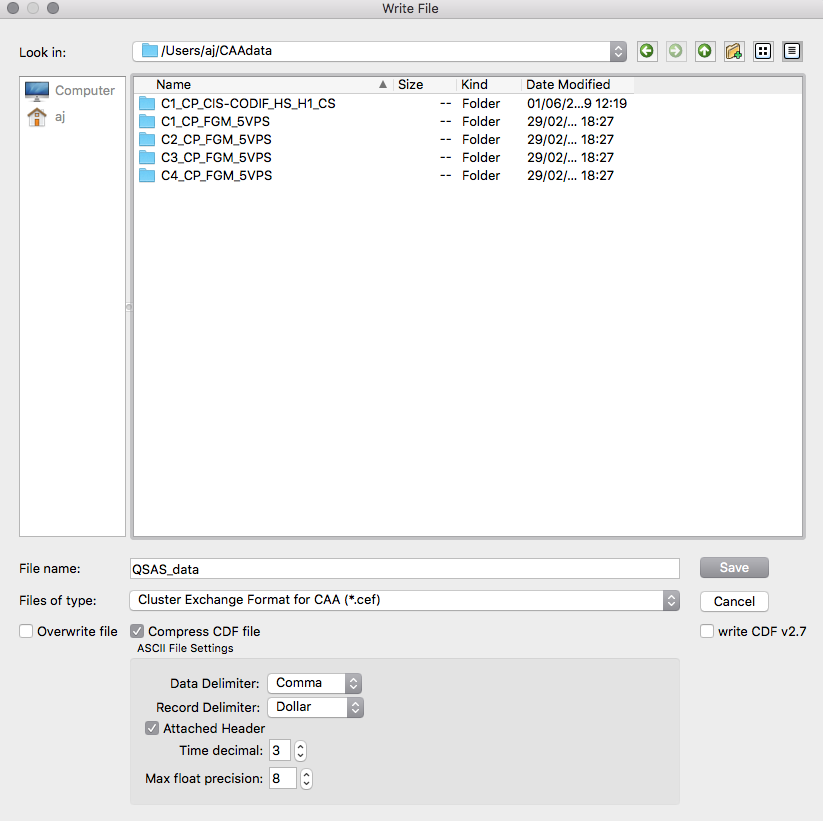
On selecting Export a dialogue appears
allowing the
user to choose the file name and directory (QSAS will make
an automatic choice by
default) and provides a check box to indicate whether an
identically named file
should be overwritten or the export aborted (to allow the user to
specify a
new, unique name). The bottom selection slot allows the user to
choose the file
type to be written. If one of the ASCII types is chosen the panel
on the right
will affect the choices for these files. Note: at present
these options
always appear active even if they have no effect on the file type
selected.
In the Direct Import window, all quantities identified as variables in the data file are shown. In CDF files, and their QSAS ASCII equivalents, many of these do not vary with records, and include labelling and other information. These do not need to be separately ingested unless the user needs them for other purposes.
When Time Series data are imported the time tag variable (usually denoted "epoch" in CDF files) is automatically ingested at the same time. The time tags will not appear on the working list, but are kept internally as cross references to the data objects.
Foreign ASCII files can usually be imported by first writing a simple ASCII header to describe the variables, file format, and time specification. These headers are described in other documentation.
Last up-dated: October 2016 Tony Allen